 |
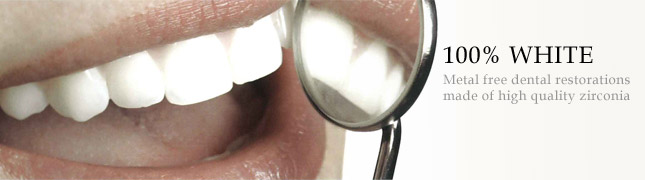
| 1.100% WHITE |
 |
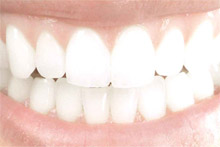 Zirconia is the oldest and most abundant element in the earth's crust and it is the base for zirconium di oxide (yttrium oxide stabilized zirconium oxide). This firstclass-performance material was successfully used for more than 20 years-for example in hip surgery and it is now also available for the dental industry. Due to its excellent health-friendly characteristics, zirconia is nowadays the preferred material of modern dental restorations among dental ceramic materials available today. Zirconia is the oldest and most abundant element in the earth's crust and it is the base for zirconium di oxide (yttrium oxide stabilized zirconium oxide). This firstclass-performance material was successfully used for more than 20 years-for example in hip surgery and it is now also available for the dental industry. Due to its excellent health-friendly characteristics, zirconia is nowadays the preferred material of modern dental restorations among dental ceramic materials available today. |
topへ戻る |
| 2.THE ADVANTAGES |
 |
 ●High translucency ●High translucency
●Possibility to colour the frame structures
individually with the patient's tooth colour
●No black margins
●Absolutely metal-free
●Excellent health compatibility
●Extreme solidity
●Longevity |
topへ戻る |
3.AESTHETICS
AND NATURALNESS |
 |
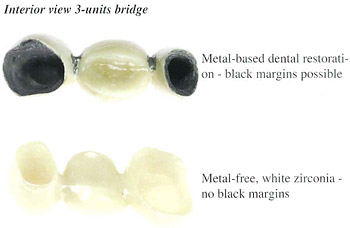 Zirconia's high translucency enhanced by the possibility to colour the frame structures with the individual patient's tooth colour favours the aesthetic and natural look of dental restorations. Due to the zirconia's light colour, there are no black margins in case of age-related receding gums, as this is frequently the case with metal restorations. Zirconia's high translucency enhanced by the possibility to colour the frame structures with the individual patient's tooth colour favours the aesthetic and natural look of dental restorations. Due to the zirconia's light colour, there are no black margins in case of age-related receding gums, as this is frequently the case with metal restorations. |
topへ戻る |
4.WEARING COMFORT AND
CLEANLINESS |
 |
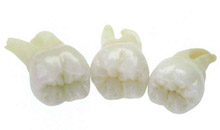 The acid resistant and non-porous material avoids the absorption of pollutants, prevents periodontitis and makes cleaning fast and easy. Excellent accuracy of fit and first-class manufacturing characteristics of the material guarantee that it is pleasant and comfortable to wear. The acid resistant and non-porous material avoids the absorption of pollutants, prevents periodontitis and makes cleaning fast and easy. Excellent accuracy of fit and first-class manufacturing characteristics of the material guarantee that it is pleasant and comfortable to wear. |
topへ戻る |
5.EXCELLENT HEALTH
COMPATIBILITY |
 |
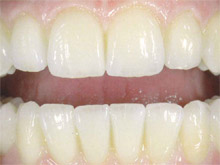 According to scientific investigations, zirconia, an absolutely metal-free material , does not release any all ergens or incompatibility in the mouth. Besides, it is particularly compatible with the mucous membrane According to scientific investigations, zirconia, an absolutely metal-free material , does not release any all ergens or incompatibility in the mouth. Besides, it is particularly compatible with the mucous membrane
and tissues as well as being gentle on the nerves, since it transfers heat and cold more slowly than dental restorations made of metal.
In addition, easy cleaning possibilities help to prevent periodontitis. |
topへ戻る |
| 6.LONGEVITY AND STABILITY |
 |
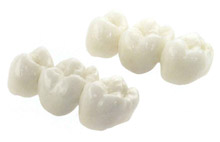 With a correct dental construction, zirconia dental With a correct dental construction, zirconia dental
restorations are an investment for life. Due to the extreme hardness and high density of the material, it
withstands the highest biting force within all the mouth areas, it does not wear off and so its colour remains unchanged. |
topへ戻る |
| 7.100% ZIRCONIA |
 |
 Natural appearance, stability and comfort starting from crowns up to large-span bridges - zirconia meets all requirements of high-quality, durable dental restorations and retains a fresh, and soigne appearance. Natural appearance, stability and comfort starting from crowns up to large-span bridges - zirconia meets all requirements of high-quality, durable dental restorations and retains a fresh, and soigne appearance.
Endow yourself and your loved ones with a carefree smile! |
topへ戻る |
8.FACTS AND POSSIBILITIES
|
 General General
What is zirconia?
Zirconia (ZrSiO4), a mineral belonging to the mineral class or Silicates, was discovered in 1789 by the German chemist M. H. Klaproth. Zirconium dioxide (ZrO2) is a compound of the element zirconium occurring in nature and has been used since
the mid 90's in prosthetic dentistry. In colloquial terms, it is abbreviated as zircon oxide or simply zirconia. With zirconia, any dental restoration can be manufactured, from single crowns up to 14-units bridges.
Not all zirconia is equal - Zirconia from Zirkonzahn
In the headquarters of Zirkonzahn, amidst the South Tyrolean mountains, zirconium powder is refined by means of a special procedure and pressed into blanks. Out of the still "soft" zirconia blank, the dental restoration is milled in the desired form at the dental laboratory and then burnt in a sintering furnace at 1500°C. Only by this combustion procedure, zirconia attains its final hardness and resistance. The purity of the material is crucial for its solidity and biocompatibility. Our high-quality raw material is characterized by exceptional bending strength, hardness and a constant dimensional accuracy. A constant shrinking value during combustion is the basis of both the highest fit precision and comfort. Zirkonzahn manufactures zirconia with different translucency features (transparency characteristics). The more transparent Prettau zirconia is particularly suitable for full zirconia restorations.
Which types of dental restorations are there?
Dental prosthesis, in colloquial terms called "false teeth", are used in principle to improve or re-establish the appearance, the language or the chewing function after the loss of one or several teeth . A distinction is made between removable and fixed dental prosthesis. Both types can be combined, as well.
Fixed dental prosthesis, which is firmly embodied in the mouth , best corresponds to the natural "feel of the mouth", since the chewing and speech function can be reconstructed almost completely. Cemented in the mouth, the patient usually accustoms himself rapidly to the fixed construction and no longer feels it as a foreign body. Crowns, bridges and implant work belong to fixed
dental restorations.
Destroyed tooth areas, which can no longer be provided with a filling, are entirely (full crown) or partially (partial crown) reconstructed by means of a crown. In order to be able to apply a crown to the damaged tooth, at first the dentist processes and grinds it, in order to create sufficient surface area for the later construction.
A bridge replaces one or more teeth and is fastened to neighbouring teeth . If a fixed dental restoration is not possible for different reasons (e.g. neighbouring teeth are too weak or arc too damaged) , then one should resort to a removable prosthesis in the form of partial or full denture. Partial prostheses can be supported by the teeth still existing in the mouth, full prostheses on the other
hand are used for edentulous cases.
An implant is screwed in the jaw as an artificial tooth root. The implant must be fixed on it together with the bone. Its function, therefore, similar to a dowel in the wall, is the anchorage of crowns and bridges.
Which materials are used for dental restorations?
Amalgam:
Amalgam is an alloy made of mercury and other metals and is used as a filling material only after the caries is removed from the damaged tooth. Due to the mercury content allergic reactions can arise.
Precious metal alloys:
The most common variants are gold platinum or palladium alloys. Precious metal is very compatible, extremely long-lasting and resistant in the patient's against other materials (acids or saliva). Precious metals, however, are heat and cold conducting and can therefore lead to sensitivity reactions.
Non precious metal alloy:
Cobalt-based or nickel-based alloys are used in particular in the field of removable dental prosthesis. Allergic reactions to the alloy components are possible.
Ceramics:
Ceramics have many positive characteristics such as high biocompatibility, natural appearance and colour fastness , and therefore are extremely suitable for dental prosthesis is work, fillings and implants. Zirconia is a high performance ceramic and is ideal for use in manifold applications of dental restorations.
Resin (also called Composite):
Dental restoration made of resin can be coloured in the tooth colours, however it is not particularly resistant. Besides, allergies and discolorations can occur. |
topへ戻る |
9.BEFORE-AFTER WARDS
|
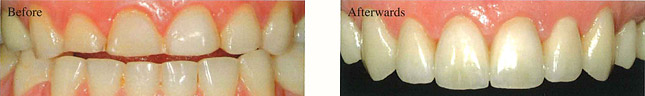
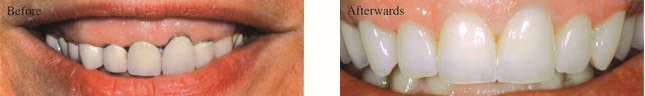
 The teeth accidentally chipped have been restored. The female patient wanted a radiant, bright and authentic looking dental prosthesis. This could be achieved by using zirconia. The teeth accidentally chipped have been restored. The female patient wanted a radiant, bright and authentic looking dental prosthesis. This could be achieved by using zirconia.
Nely, 36 - Mexico City, Mexico |
 |
| |
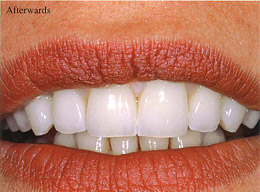 One of the advantages of zirconia is that no black margins are visible at the edge of the gums in the event they begin to recede. This can occur wilh a traditional metal dental prosthesis. One of the advantages of zirconia is that no black margins are visible at the edge of the gums in the event they begin to recede. This can occur wilh a traditional metal dental prosthesis.
Maria. 38 - Milall, Italy |
 |
topへ戻る |
|



